Vuex 是什么
Vuex 是一个专为 Vue.js 应用程序开发的全局状态管理库,采用集中式存储管理应用的所有组件的状态,解决多组件数据通信
- Vue 官方搭配,专属使用 (类似于:vue-router),有专门的调试工具
- 集中式状态方案(操作更简洁)
data() { return { 数据, 状态 }}
- 数据变化是可预测的(响应式)
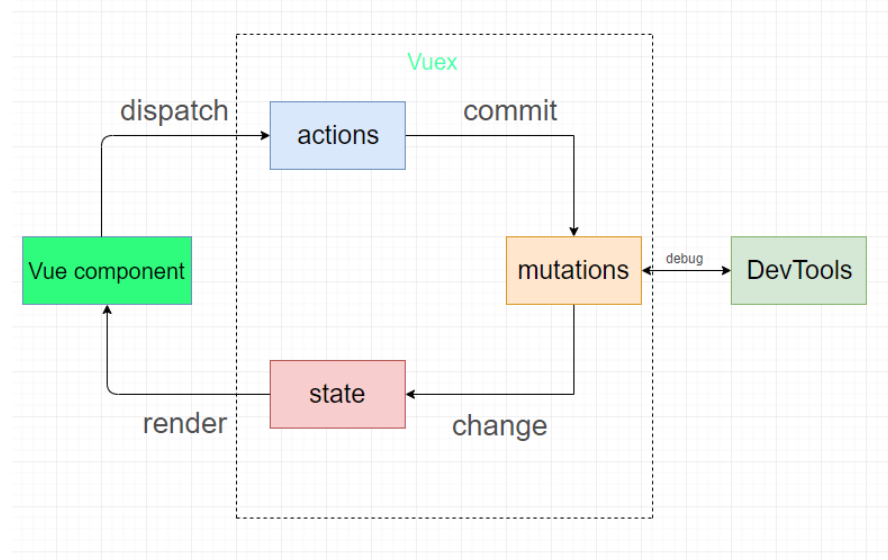
使用方法
在vuex 中this 指的是 store 实例, 可以通过 this.state 访问 state
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {
count: 0
},
mutations: {
increment (state) {
state.count++
}
}
})
export default store
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
import store from './store/index.js'
new Vue({
el: '#app',
store: store,
})
|
核心概念
state
- 在组件中,通过
this.$store.state.属性名 来访问
- 在模板中,可以省略
this,直接写成:{{$store.state.属性名}}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| new Vuex.store({
state: ()=>{
return {
属性名:属性值
}
}
})
|
getters
- 在组件中通过
this.$store.getters.getter的名字 来访问
- 在模板中,可以省略
this,直接写成:{{$store.getters.getter的名字}}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| new Vuex.store({
getters: {
getter的名字1: function (state) {
return 要返回的值
},
},
})
|
mutations
mutations 中的每一项都是一个函数,每个函数有两个形参
- 第一个参数表示当前的 state,Vuex 内部传入的
- 第二个参数表示载荷,表示在调用 mutation 时传入的实参
调用方式
- 在组件中使用 this.$store.commit(‘mutations的名字’, 参数)
- 在 actions 中通过 context.commit(‘mutations的名字’, 参数)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| new Vue.store({
mutations: {
mutation名1: function(state, 载荷) {
},
mutation名2: function(state, 载荷) {
},
}
})
|
actions
- 在组件中通过
this.$store.dispatch('actions的名字', 参数)
- 在模板中,可以省略
this,直接写成:{{$store.dispatch.actions的名字}}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| new Vuex.store({
actions: {
action的名字: function (context, 载荷) {
},
},
})
|
modules
问题导入:
- 随着项目越来越大,需要放在 vuex 中的数据越来越多,整个 store/index.js 中代码会越来越长,怎么办呢?
modules 的作用:
多模块
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
| export default new Vuex.Store({
state: {},
getters: {},
mutations: {},
actions: {},
modules: {
模块名1:{
namespaced: true,
state: {},
getters: {},
mutations: {},
actions: {},
modules: {}
},
模块名2:{
state: {},
getters: {},
mutations: {},
actions: {},
modules: {}
}
}
})
|
也可以更进一步对文件进行拆分
|–store /
|——- index.js # 引入模块
|——- modules
|————– / mod1.js # 模块1
|————– / mod2.js # 模块2
1
2
3
4
5
6
| modules: {
mod1.js,
mod2.js
}
|
语法调整
1
2
| 获取数据项: {{$store.state.模块名.数据项名}}
获取getters:{{$store.getters['模块名/getters名']}}
|
访问模块中的 mutations/actions
如果 namespaced 为 true,则需要额外去补充模块名
如果 namespaced 为 false,则不需要额外补充模块名
1
2
| $store.commit('mutations名')
$store.commit('模块名/mutations名')
|
小结
使用了 modules 之后,在访问数据时就要额外添加 modules 的名字了
结论:在使用 modules 时,建议都给加上 namespaced!
结构优化
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
const module1 = {
namespaced: true,
state: {},
getters: {},
mutations: {},
actions: {},
modules: {}
}
export default module1
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
const module2 = {
state: {},
getters: {},
mutations: {},
actions: {},
modules: {}
}
export default module2
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
import module1 from './modules/module1'
import module2 from './modules/module2'
Vue.use(Vuex)
export default new Vuex.Store({
state: {},
getters: {},
mutations: {},
actions: {},
modules: {
module1,
module2
}
})
|
辅助函数
mapState
- 直接使用:
this.$store.state.state属性名
映射 辅助函数mapState
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
import { mapState } from 'vuex'
computed: {
...mapState(['state属性名']),
...mapState({'新名字': 'state属性名'})
}
|
mapGetters
- 直接使用:
this.$store.getters.getters名字
mapGetters 辅助函数
1
2
3
4
5
6
| {
computed: {
...mapGetters(['getters名字']),
...mapGetters({'新名字': 'getters名字'})
}
}
|
mapMutations
- 直接使用:
this.$store.commit('mutation名', 参数)
mapMutations 辅助函数
1
2
3
4
5
6
| {
methods: {
...mapMutations(['mutation名']),
...mapMutations({'新名字': 'mutation名'})
}
}
|
mapActions
- 直接使用:
this.$store.dispatch('action名', 参数)
mapActions 辅助函数
1
2
3
4
5
6
| {
methods: {
...mapActions(['actions名']),
...mapActions({'新名字': 'actions名'})
}
}
|
moudle访问指定模块
开启namespaced : namespaced: true
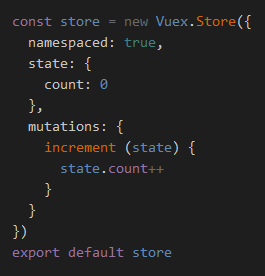
2.namespaced语法变化
原始语法
- 全局的:指的是 store/index.js里面的 state、mutations、actions
- 模块的:指的是模块内部的 state、mutations、actions
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
全局的: $store.state.数据项名
模块的: $store.state.模块名.数据项名
全局的: $store.getters.getter名
模块的: $store.getters['模块名/getters名']
全局的: $store.commit('mutations名',载荷)
模块的: $store.commit('模块名/mutations名',载荷)
全局的: $store.dispatch('actions名',载荷)
模块的: $store.dispatch('模块名/actions名',载荷)
|
state
- 直接使用:
this.$store.state.模块名.xxx
- map 辅助函数
1
2
3
4
5
| {
computed: {
...mapState('模块名', ['xxx']),
}
}
|
getters
- 直接使用:
this.$store.getters.模块名.xxx
- map 辅助函数
1
2
3
4
5
6
| {
computed: {
...mapGetters('模块名', ['xxx']),
...mapGetters('模块名',{'新名字': 'xxx'})
}
}
|
mutations
- 直接使用:
this.$store.commit('模块名/mutation名', 参数)
- map 辅助函数
1
2
3
4
5
6
| {
methods: {
...mapMutations('模块名', ['xxx']),
...mapMutations('模块名',{'新名字': 'xxx'})
}
}
|
actions
- 直接使用:
this.$store.dispatch('模块名/action名', 参数)
- map 辅助函数
1
2
3
4
5
6
| {
methods: {
...mapActions('模块名', ['xxx']),
...mapActions('模块名',{'新名字': 'xxx'})
}
}
|
总结
辅助函数语法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
全局的: ...mapState(['数据项名'])
模块的: ...mapState('模块名', ['数据项名'])
更改属性名: ...mapState('模块名', {'新名字': 'xxx'})
全局的: ...mapGetters(['数据项名'])
模块的: ...mapGetters('模块名', ['数据项名'])
更改属性名: ...mapGetters('模块名',{'新名字': 'xxx'})
全局的: ...mapMutations(['mutaion名'])
模块的: ...mapMutations('模块名', ['mutaion名'])
更改属性名: ...mapMutations('模块名',{'新名字': 'xxx'})
全局的: ...mapActions(['action名'])
模块的: ...mapActions('模块名', ['action名'])
更改属性名: ...mapActions('模块名',{'新名字': 'xxx'})
|
vuex-persistedstate 持久化
下载插件
1
| npm install --save vuex-persistedstate@3.2.1
|
在vuex中配置插件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
| import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
import creteState from 'vuex-persistedstate'
Vue.use(Vuex)
export default new Vuex.Store({
plugins: [creteState()],
state: {
token: '',
},
mutations: {
updateToken(state, newToken) {
state.token = newToken
},
},
actions: {
},
modules: {
}
})
|
子模块访问根节点
state
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| const moduleA = {
namespaced: true,
state: () => ({
someData: 'ModuleA data'
}),
getters: {
someRootData(state, getters, rootState) {
return rootState.someRootData
}
}
}
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {
someRootData: 'Root data'
},
modules: {
a: moduleA
}
})
|
getters
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| const moduleA = {
namespaced: true,
getters: {
someRootGetter(state, getters, rootState, rootGetters) {
return rootGetters.someRootGetter
}
}
}
const store = new Vuex.Store({
getters: {
someRootGetter: (state) => {
return 'Root getter value'
}
},
modules: {
a: moduleA
}
})
|
带参数的 getters
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
| const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {
users: [
{ id: 1, name: 'Alice' },
{ id: 2, name: 'Bob' },
{ id: 3, name: 'Charlie' }
]
},
getters: {
getUserById: (state) => (id) => {
return state.users.find(user => user.id === id)
}
}
})
computed: {
user() {
return this.$store.getters.getUserById(2)
}
}
const user = store.getters.getUserById(2)
console.log(user)
|
actions
调用根模块的 action 并传递参数 dispatch(‘根模块actions名’, payload, { root: true })
在子模块的 actions 中访问根模块的 state 和 getters
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
| const moduleA = {
namespaced: true,
actions: {
someAction({ state, commit, rootState, rootGetters }) {
console.log(rootState.someRootData)
console.log(rootGetters.someRootGetter)
dispatch('someRootAction', null, { root: true })
}
}
}
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {
someRootData: 'Root data'
},
getters: {
someRootGetter: (state) => 'Root getter value'
},
modules: {
a: moduleA
}
})
|
在子模块的 actions 中调用根模块的 mutations 和 actions
调用根模块的 mutations 并传递参数 commit(‘根模块mutations名’, 参数, { root: true })
mutations
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
| const moduleA = {
namespaced: true,
actions: {
someAction({ commit, dispatch }) {
commit('someRootMutation', null, { root: true })
}
}
}
const store = new Vuex.Store({
mutations: {
someRootMutation(state) {
console.log('Root mutation called')
}
},
actions: {
someRootAction({ commit }) {
console.log('Root action called')
}
},
modules: {
a: moduleA
}
})
|
总结
vuex中有哪些配置项(核心概念)作用是什么
- state作用: 负责存储数据
- getters作用:state计算属性(有缓存)
- mutaions作用:负责同步更新state数据
- mutaions是唯一可以修改state数据的方式
- actions作用:负责异步操作,例如发送网络请求,将请求到的数据通过commit触发mutaions来修改state
- modules作用:负责模块化管理vuex数据
如果直接在页面中或者actions中修改state里面的数据报错吗?
不会,但是直接修改 state 的代码无法被 Vuex 的调试工具(如 Vue DevTools)正确追踪和记录,难以调试应用中的问题
如果你在异步操作中直接修改了 state,可能导致状态不一致,因为异步操作可能在不同的时间段触发多次状态修改
什么情况下只能通过mutations修改state
开启vuex 严格模式,如果使用其他方式更改state会报错
严格模式主要用于开发环境,它可以帮助你确保所有状态修改都遵循 Vuex 的最佳实践。通过捕捉不合法的状态修改,可以在开发早期发现潜在的错误,避免难以调试的状态管理问题
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {
count: 0
},
mutations: {
increment(state) {
state.count++;
}
},
strict: true
})
|


